About the Subject Overview
Liberal Studies(S4 to S6)
Background:
Liberal Studies is one of the core subjects in the three-year senior secondary curriculum. The subject aims to broaden students’ knowledge base and enhance their social awareness through the study of a wide range of issues. The modules selected for the curriculum focus on themes of significance to students, society and the world, designed to enable students to make connections across different fields of knowledge and to broaden their horizons. The learning experiences provided will foster students’ capacity for life-long learning, so that they can face the challenges of the future with confidence.
The aims of Senior Secondary Liberal Studies are:
| a. | to enhance students’ understanding of themselves, their society, their nation, the human world and the physical environment; |
| b. | to enable students to develop multiple perspectives on perennial and contemporary issues in different contexts (e.g. cultural, social, economic, political and technological contexts); |
| c. | to help students become independent thinkers so that they can construct knowledge appropriate to changing personal and social circumstances; |
| d. | to develop in students a range of skills for life-long learning, including critical thinking skills, creativity, problem-solving skills, communication skills and information technology skills; |
| e. | to help students appreciate and respect diversity in cultures and views in a pluralistic society and handle conflicting values; and |
| f. | to help students develop positive values and attitude towards life, so that they can become informed and responsible citizens of society, the country and the world. |
Interface with Basic Education and Post-secondary Pathways :
Liberal Studies builds on what students have learnt in basic education. Through exploring themes important to the modern world, it helps students to extend their breadth of knowledge, depth of understanding, independent thinking skills and ability to make connections.The study of Liberal Studies enables students to explore different pathways for further studies and future careers. Liberal Studies will help to foster intellectual ability in general, and develop multiple perspectives that will be of benefit to students in further studies at the tertiary level. The civic literacy, social awareness and ability to make informed decisions that students will have developed will also prepare them for effective learning and wise decision making in the ever-changing work environment.
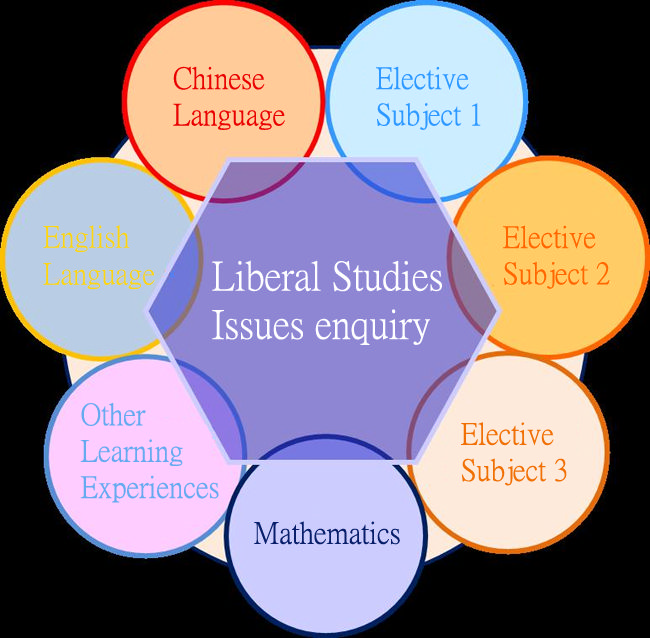
Overall Structure:
Liberal Studies builds on what students have learnt in basic education. Through exploring themes important to the modern world, it helps students to extend their breadth of knowledge, depth of understanding, independent thinking skills and ability to make connections.| Areas of Study | Module | Independent Enquiry Study (IES) | ||||||||||||
 |
|
Students are required to conduct an IES making use of the knowledge and perspectives gained from the three Areas of Study and extending them to new issues or contexts. To help students develop their IES titles, the following themes are suggested:
|
Linkages among the Areas of Study:
The three Areas of Study are not independent fields of knowledge or self-contained disciplines. They have inter-connections among them. Students are encouraged to apply the understandings and perspectives developed in one area to the study of the others whenever appropriate.Basic Design of Modules:
Each module is organised around a central concept relevant to the Area of Study, with key themes relevant to students' lives identified. The "questions for enquiry" suggested under each theme show possible pathways for exploring into these contemporary and perennial issues. These guiding questions also indicate the expected breadth and depth of the enquiry.Area of Study: Self and Personal Development
Module 1: Personal Development and Interpersonal RelationshipsThemes |
Key Questions for Enquiry |
Related values and attitudes |
1. Understanding oneself |
What challenges and opportunities does a person have during adolescence? |
adaptability to change, responsibility, self-esteem, self-reflection, rationality, self-discipline, independence |
2. Interpersonal relationships |
What interpersonal factors facilitate adolescents to reflect upon and prepare for the transition to adulthood? |
Cooperation, gender equity, empathy, integrity, self-reflection, self-determination, respect for self, respect for others, social harmony, sense of responsibility, interdependence |
Area of Study: Society and Culture
Module 2: Hong Kong TodayThemes |
Key Questions for Enquiry |
Related values and attitudes |
1. Quality of life |
Which directions might be chosen in maintaining and improving Hong Kong residents’ quality of life? |
respect for quality and excellence; sustainability; rationality; sensitivity; care and concer |
2. Rule of law and socio-political participation |
How do Hong Kong residents participate in political and social affairs and come to grips with rights and responsibilities with respect to the rule of law? |
respect for the rule of law; participation; human rights and responsibilities; democracy; justice |
3. Identity |
How are the identities of Hong Kong residents developed? |
sense of belonging; plurality; open-mindedness; individuality; interdependence |
Module 3: Modern China
Themes |
Key Questions for Enquiry |
Related values and attitudes |
1. China’s reform and opening-up |
What impact has reform and opening-up had on the overall development of the country and on people’s life? |
solidarity; patriotism; sustainability; human rights and responsibilities; care and concern; justice |
2. Chinese culture and modern life |
With respect to the evolution of concepts of the family, what |
culture and civilisation heritage; respect for different ways of life, beliefs and opinions; plurality; sensitivity; appreciation |
Module 4: Globalization
Themes |
Key Questions for Enquiry |
Related values and attitudes |
1. Impact of globalization and related responses |
Why do people from different parts of the world react differently to the opportunities and challenges brought by globalization? |
interdependence; justice; cooperation; culture and civilization heritage; plurality; adapting to changes; open-mindedness; empathy; participation; mutuality |
Area of Study: Science, Technology and the Environment
Module 5: Public HealthThemes |
Key Questions for Enquiry |
Related values and attitudes |
1. Understanding of public health |
How is people’s understanding of disease and public health affected by different factors? |
valuing the suggestions of others; respect for evidence; respect for different ways of life, beliefs and opinions; cultural heritage |
2. Science, technology and public health |
To what extent does science and technology enhance the development of public health? |
betterment of humankind; human rights and responsibilities; cooperation; moral considerations |
Module 6: Energy Technology and the Environment
Themes |
Key Questions for Enquiry |
Related values and attitudes |
1. The influences of energy technology |
How do energy technology and environmental problems relate to each other? |
Betterment of humankind; respect for evidence; interdependence |
2. The environment and sustainable development |
Why has sustainable development become an important contemporary issue? What is the relationship between its occurrence and the development of science and technology? |
Responsibility; caring for the living and non-living environments; betterment of humankind; sustainability; simplicity |
Independent Enquiry Study (IES):
As an integral part of the curriculum of Liberal Studies, the IES contributes to the curriculum aims by:a. providing an opportunity for students to learn to become self-directed learners responsible for their own learning;
b. enhancing students’ ability to connect, integrate and apply knowledge, perspectives and skills developed through the three Areas of Study;
c. helping students develop higher-order thinking skills and communication skills through investigative exploration of issues; and
d. broadening students’ horizons and catering for their interests and inclinations.
The IES has to be investigative and involve the following three stages:
Stage I :- Selection of study area / theme
- Collection of background information
- Confirmation of the question for enquiry
- Design of work plan and schedule
- Collection of data / other kinds of information
- Organisation of data / other kinds of information
- Analysis of data / information
- Evaluation of different points of view
- Presentation of IES results, amendments according to feedback
- Writing up of study report, adoption of suitable ways to show the results of the study
Assessment
Assessment Objectives
The assessment objectives of Liberal Studies, which are aligned with the broad learning outcomes. Some of the assessment objectives are applicable to both internal and public assessment, while others are applicable to only one of these two modes:- demonstrate a sound understanding of the key ideas, concepts and terminologies of the subject;
- make conceptual observations from information resulting from enquiry into issues;
- apply relevant knowledge and concepts to contemporary issues;
- identify and analyse the interconnectedness and interdependence amongst personal, local, national, global and environmental contexts;
- recognise the influence of personal and social values in analysing contemporary issues of human concern;
- draw critically upon their own experience and their encounters within the community, and with the environment and technology;
- discern views, attitudes and values stated or implied in any given factual information;
- analyse issues (including their moral and social implications), solve problems, make sound judgments and conclusions and provide suggestions, using multiple perspectives, creativity and appropriate thinking skills;
- interpret information from different perspectives;
- consider and comment on different viewpoints in their handling of different issues;
- self-manage and reflect upon the implementation of successive stages of the enquiry learning process in terms of time, resources and attainment of the objectives of the enquiry;
- communicate clearly and accurately in a concise, logical, systematic and relevant way;
- gather, handle and analyse data and draw conclusions in ways that facilitate the attainment of the objectives of the enquiry;
- demonstrate an understanding and appreciation of different cultures and universal values;
- demonstrate empathy in the handling of different issues.
Public Assessment design
There are two components of the public assessment of LS, including Public Examination and School-based assessment (SBA). For details, please refer to the table below outlining the various components of the public assessment of LS:Component |
Part |
Weighting |
Duration |
Public |
Paper 1 Data-response questions |
50% |
2 hours |
Paper 2 Extended-response |
30% |
1 hour and 15 minutes |
Public examinations
Paper 1 This paper consists of data-response questions, all of which will have to be answered.Paper 2 Extended-response questions ,this paper consists of extended-response questions. Candidates will be required to answer one question only.
School-based assessment (SBA)
The Independent Enquiry Study (IES) is adopted as the mode of SBA in Liberal Studies. The IES is an investigative study in which students are required to demonstrate various skills such as problem-solving, data gathering and analysis, and communication. Each IES project should include a certain amount of subject matter based on students’ reading, research and personal experiences. Students can carry out an enquiry-based project, and the main body of the project can be in written or non-written form. The latter should be accompanied by a short written text explaining the main idea of the project, and showing the student’s reflections on it. The HKEAA has launched a dedicated webpage, “Public Assessment of HKDSE Liberal Studies” in order to provide an easy access to a wide range of resources for teachers e.g. The assessment framework, the format and content of the examination, School-based Assessment (SBA), marking and grading, and exemplars that demonstrating different level of performance, etc.L&T Resources
Learning resources include not only the learning and teaching resources found on this Resource Platform, and publications and audio-visual teaching aids produced by other organisations, but also web-based learning materials, IT software, the Internet, the media, resources in the natural environment, people, libraries, etc. All of these should be drawn upon to help students to learn, broaden their learning experiences and meet different learning needs. If used effectively, they will help students to consolidate what they have learnt, extend and construct knowledge for themselves, develop the learning strategies and generic skills they need, and reflect on their values and attitudes. Teachers can also make use of learning resources to provide scaffolding for knowledge construction that goes beyond their confines, thus supporting students’ learning to learn.
In selecting and adapting the learning and teaching materials, teachers should take the following three aspects into consideration, namely, multiple perspectives, pluralistic pedagogies and alignment with different learning and teaching activities. As for multiple perspectives, teachers should try their best to collect different stakeholders’ opinions on the issue and avoid over-emphasising any specific stance. Regarding pluralistic pedagogies, students vary in terms of the knowledge, abilities, and learning styles they have. Therefore, teachers should cater to such learner differences in order to arouse student interest and enhance their learning effectiveness. Teachers should select materials in alignment with different learning and teaching activities and note the nature of the materials, or even consider giving appropriate teaching instructions or verbal hints as aids to support student learning.
The EDB will continue to upload learning and teaching resources on this Platform for the reference of teachers.